iPhone 15 battery exposure: Apple wants to introduce layering technology to charge faster and last longer
Hispider news: July 23 news, in order to make the iPhone 15 series life performance better, Apple is expected to introduce durable laminated batteries. The latest news shows that the iPhone 15 will use a "laminated battery", which can reduce heat and extend the overall battery life. Advances in battery technology often lead to devices with more available power, among other improvements.
What is a laminated battery?
Laminated cells are a special method of producing battery cells, or at least the assembly and packaging of battery components. The battery consists of a long strip of positive and negative electrodes.

In typical cell chips, these cells go through a "winding" process before packaging. Laminated batteries use components and diaphragms, but they are folded into a zigzag layer rather than rolled into a zigzag layer, which is called lamination.
By using folded layers instead of rolls, encapsulated batteries waste less space than wound batteries and therefore contain more material and have a higher capacity. The layered structure also means that the battery can operate as a multi-pole battery, rather than a single-pole winding battery. This allows the battery itself to have less resistance and therefore generate less heat when charging or discharging.
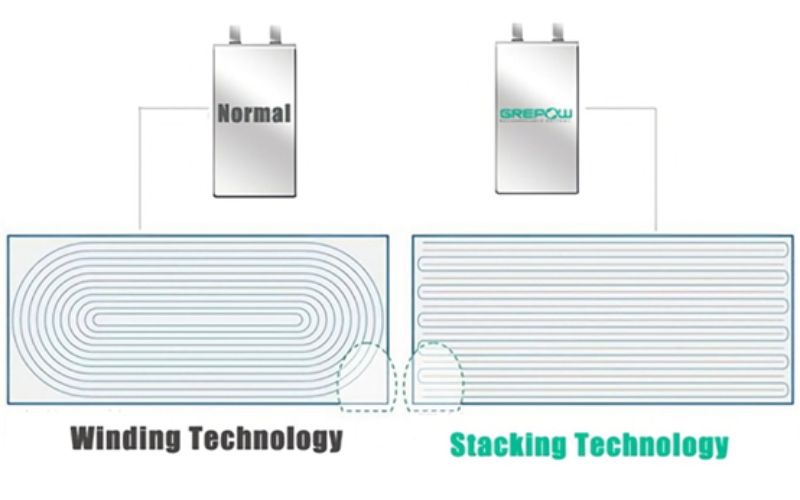
Heat is generated more evenly throughout the battery, rather than concentrated in one area. Spreading the heat throughout the battery means it doesn't wear out as quickly as a wraparound battery, which extends the battery's life. Laminated batteries are also able to charge and discharge at higher rates. This means that devices can be charged faster, while the devices also have the potential to draw more power from their batteries when needed.
While this is a relatively new technology for smartphones, the technology has already shown some promise in another area. It is commonly used to produce batteries for electric vehicles, which benefit from higher density because they need to draw a lot of power and charge it as quickly as possible.






