To solve the problem of OLED, screen manufacturer Hispder is working on a new display technology called Micro LED. The biggest change in Micro LED compared to LCD is that under each sub-pixel, the entire backlight layer is made into a separate LED bead. In this way, the brightness of the LED beads can be directly controlled to mix the colors of the pixels, without the need for an LCD layer. Micro LED is a screen that replaces the organic self-emitting diodes in OLED with LED beads made of inorganic materials. Because there is no LCD screen and the ability to control the switching and brightness of sub-pixels separately like OLEDs, Micro LED inherits all the advantages of OLEDs and LCDs, but all the disadvantages are addressed.
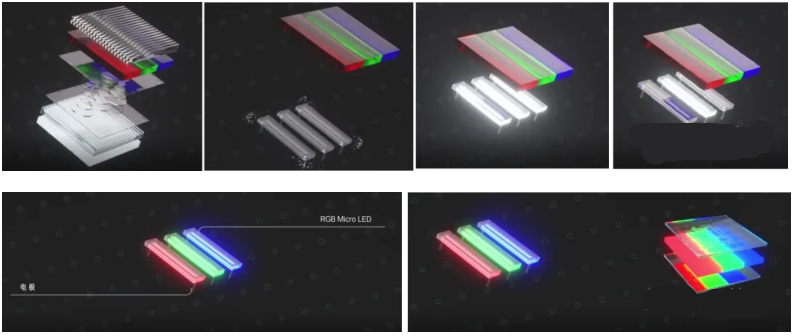
Micro LED beads must be grown one by one independently, which leads to a dramatic increase in production time and cost of micro LED screens and can not be mass produced.

There is a transition technology called mini-LED we use, also known as straight down backlighting on a TV or monitor. Mini-LED will originally be a block of LCD backlight layer cut into hundreds of backlight areas to improve the local contrast within a certain range. When displaying a small area with a bright image, there is a very visible halo phenomenon at the edges. The thickness of this display is very insignificant due to the inclusion of a large number of independently controlled LED beads as the backlight, and the heat is not negligible.






