Hispider tells you comprehensively how the phone screen is composed
First, the shape of the mobile phone screen
Since smartphones have occupied the mainstream market, mobile phones, as entertainment and information centers in fragmented time, require a larger display area, so the screen is getting bigger and bigger. At the same time, traditional phones have a "forehead" to place the handset and the front camera, and a "chin" to place the Home button, which makes the phone too large and difficult to improve the screen proportion.
Later, Apple thought of a way to concentrate a series of devices on the forehead of the phone to the center, and let the screen extend on both sides, which looks like "Qi bangs", so this screen is called "bangs screen".
The iPhone's iconic bangs screen
"Bangs screen" started the first shot in the war of mobile phone screen proportion. Various Android phones followed suit, but quickly became ugly and boring, so various designs with higher screen ratios appeared.
Water drop screen: The top of the screen avoids the front camera, and the black background color of the camera and the top border are connected, like hanging a shaky water drop, so it is named "water drop screen".
The Droplet screen for Android phones”
Pearl screen: In fact, it is a water drop screen, but Huawei feels that the part occupied by the camera is more like a full and rounded pearl, in order to highlight the extraordinary temperament, it is called "pearl screen".
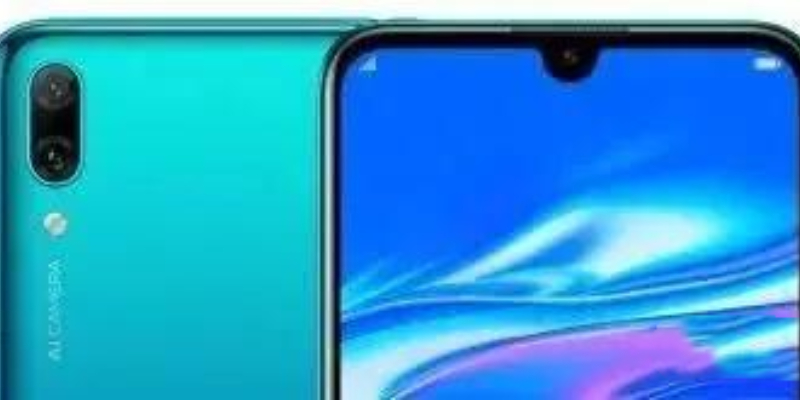

Huawei's 'pearl screen'
Hole screen: As can be seen from the previous several forms, the processing method of the front camera determines the shape of the screen. If you cut a hole in the screen and insert a camera on it, it becomes a "hole screen".

Android's 'hole screen'
Waterfall screen: The front fringe screen, water drop screen and hole digging screen all follow the camera on the mobile phone without exception, but there are still borders on both sides of the phone, and it is still not shocking enough. So someone thought of making a curved surface on the left and right sides, bending the screen down a little, not from the front not see the border! The left and right sides of this screen are like waterfalls, hence the name "waterfall screen".
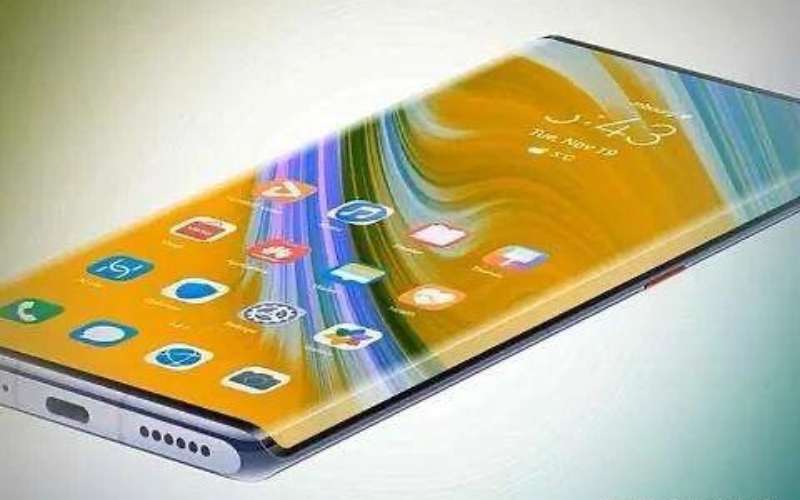

Android 'waterfall screen'
Full screen: The front of the phone is a complete screen, no bangs, no drops or pearls, and no holes. The full-screen screen seems perfect, but it is achieved by a series of compromises: the front-facing camera usually shrinks inside the body, and slowly pops out from the top when in use, this structure must be precise and durable, so it adds unnecessary complexity to the perfect appearance. True full screen can also be superimposed with waterfall screen.
The true 'full screen' of Android phones
Second, the main parameters of the mobile phone screen
Mobile phone screens are measured in inches, with each inch equivalent to 2.54 centimeters. Usually say the phone screen is how many inches, in fact, does not refer to the side length of the phone, but the diagonal length of the screen.
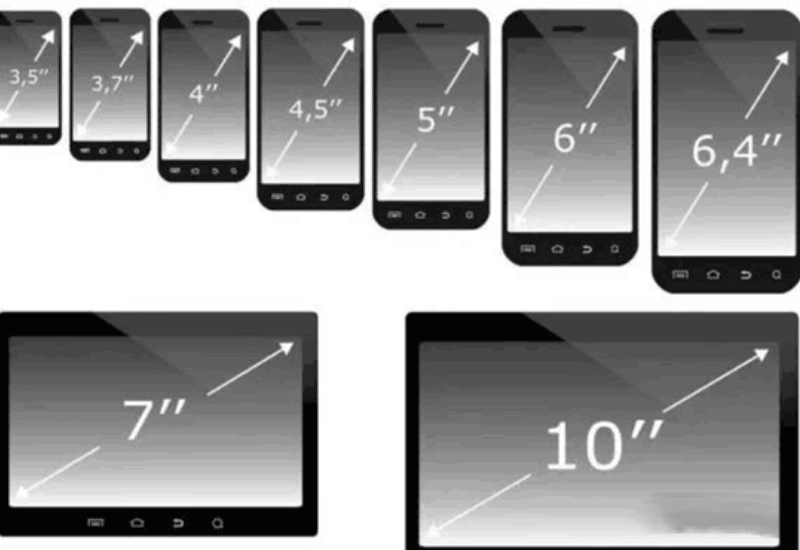
The size of the screen is measured using the diagonal length in inches
As mobile phones evolve from feature phones to smartphones, their screens are getting bigger. Once Jobs claimed that the gold size of the mobile phone screen is 3.5 inches, the result now most flagship screen size is maintained at more than 6 inches, and even many manufacturers have expanded the mobile phone screen to 7 inches.
Does a larger screen necessarily make the image clearer? This brings us to the concept of pixels and resolution.
Pixel: The principle of screen display is to divide the effective area into many small grids, each grid only shows one color, which is the smallest element of imaging, so it is called "pixel".
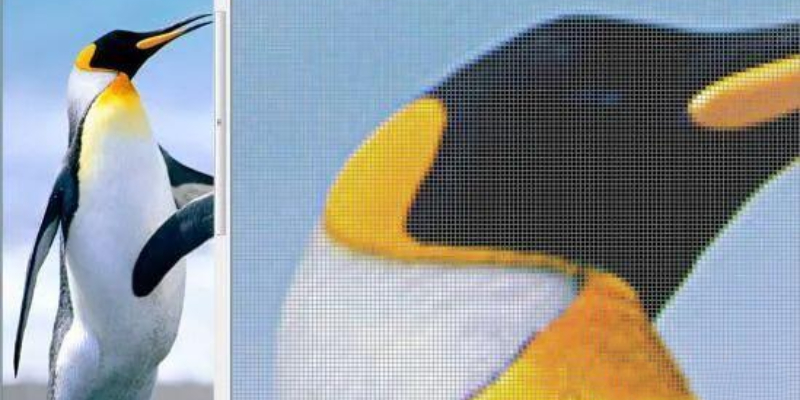

Pixels are small squares on the screen, each of which displays a color
Resolution: How many pixels the screen has in both directions, length and width, is called resolution, and is generally represented by AxB. The higher the resolution, the smaller the area of each pixel, and the smoother the display.
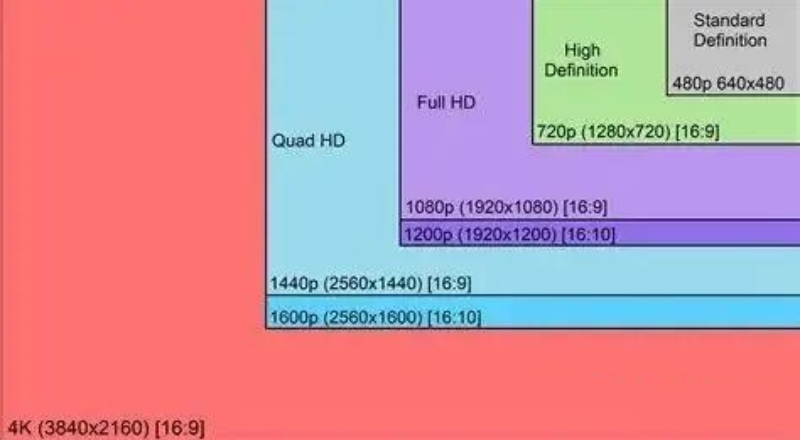
Common monitor screen resolution definitions
For example, the iPhone X has a 5.8-inch screen with a resolution of 1125x2436, which means the phone has 1,125 pixels in width and 2,436 pixels in length.
PPI: Different mobile phone screen sizes, the natural resolution is different, so how to intuitively represent the pixel density of the mobile phone screen, that is, the clarity? The answer is simple, no matter how big your screen area is, it is converted into the number of pixels per unit area, and then the standard is unified and can be compared with each other.
In fact, because the screen size is expressed in inches, the industry standard is converted to the number of Pixels Per Inch of the screen, called PPI(Pixels Per Inch), also known as pixel density. PPI is calculated as follows: Using the Pythagorean theorem, calculate the number of pixels in the diagonal direction from the number of horizontal and vertical pixels in the resolution, and then divide by the diagonal length (that is, the number of inches of the flat size of the phone).The following figure takes the iPhone5 as an example, which can be calculated to have a PPI of 326. Of course, it's easier to get the PPI value by looking at the product description.
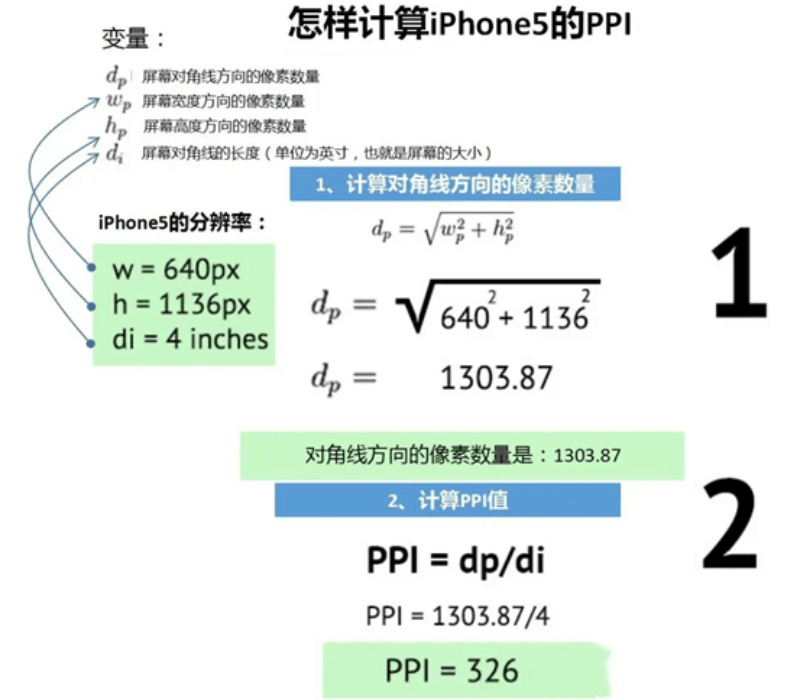
PPI Calculation Example (iPhone5)
With a measurement method, how much PPI is it good to use for mobile phone screens? The expectation, of course, is that the image will be clear and smooth to the eye, with no pixels at all perceptible.
Ten years ago, at the launch of the iPhone 4, Jobs put it this way: "When you're holding something 10-12 inches away from you, as soon as it reaches the 'magic number' of 300 PPI, your retina can't distinguish pixels."

Steve Jobs holding an iPhone4
This is Apple's original definition of "Retina screen", and the iPhone 4 screen has a pixel density of 326ppi.
In fact, Jobs' definition assumes that the person looking at the screen has a vision of 1.0, but many people have far better vision than 1.0; And the distance to look at the screen needs to be 25 to 30 centimeters, in fact many people may get closer. Therefore, the 300 PPI number is not absolute.
The industry is not limited to this value, but constantly higher, the current mainstream mobile phone PPI between 300 and 500, Samsung's flagship even more than 500, even Apple's own iPhone X and 11 have reached 458 PPI.
Let's talk about another parameter that has been heated recently: refresh rate.
Refresh rate is the number of times the phone's screen is refreshed in one second. For example, the common 60Hz refresh rate is that the content displayed on the screen is refreshed 60 times per second. Why does the content of the screen need to refresh quickly? When the object is in rapid motion, when the image seen by the human eye disappears, the human eye can continue to retain its image for about 0.1-0.4 seconds, this phenomenon is called visual retention phenomenon. Because of the visual retention effect, if you give people a number of rapidly changing pictures, the content of the previous picture is still in the visual retention, and the next picture is soon in the eye, giving people a continuous animation feeling, which is the principle of video.
Therefore, there is a "FPS: Frame per second" concept for video playback, which is how many consecutive frames are played per second.
At a frame rate of 16 FPS, the human eye perceives the image as coherent, and higher frame rates result in smoother, more realistic animations. In general, 25 to 30 FPS is acceptable, but increasing the frame rate to 60 FPS can significantly improve the sense of interactivity and realism.
Therefore, the refresh rate of the screen must be greater than the frame rate of the video. Otherwise, the video is played to the next frame, and the screen has not refreshed the display, and the user experience is naturally not good. Most current video frame rates are less than 60FPS, so the refresh rate of the phone screen should not be lower than 60Hz. In theory, the higher the refresh rate, the more delicate and smooth the display and operation of the screen, so many flagship machines are currently using 90Hz, or even 120Hz refresh rate.
Third, the technology behind the screen of the phone
If we look at the poster of the mobile phone, we can find that the words about the screen material and technology are varied: there are TFT LCD, TFT, IPS, LTPS, OLED, AMOLED, etc., which is dazzling.
How are screens using these technologies different, and what are the pros and cons?
In fact, the current mainstream mobile phone screen, from the big technology classification, is nothing more than LCD and OLED these two. LCD: English full name Liquid Crystal Display, in fact, is the famous liquid crystal display. OLED: English full name Organic Light-Emitting Diode, translated as organic light-emitting diode, also known as organic laser display. The three primary colors of light are red, green and blue, and when these three colors are mixed in different proportions, almost all colors in nature can be obtained. Therefore, every pixel on the phone screen is also composed of a mixture of these three colors.
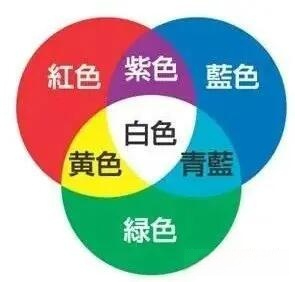
The three primary and mixed colors of light
The following is the longitudinal view of each pixel under LCD and OLED technology, indicating the principle of this pixel's light.
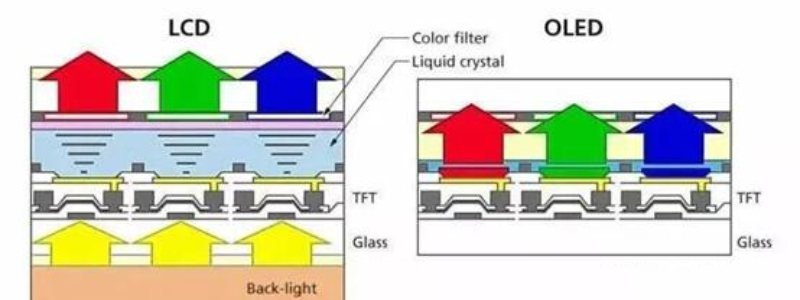
LCD and OLED screen structure
LCD technology, "Liquid Crystal (that is, liquid crystal on the left in the above picture)" the two words are very prominent, but the liquid crystal can’t emit light, need a backplane composed of LED (light emitting diode) to provide a white light source, also known as "backlight (in the above picture)". Each pixel is backlit with a thin film of red, green, and blue. White light through these films becomes red, green, and blue. However, if the intensity of these three kinds of light is the same, it will become white or gray light when mixed, so the intensity of each light must be flexibly controlled to mix a variety of colors.
At this time, it is the turn of the liquid crystal material. Liquid crystal this substance has a characteristic, that is, under the action of electric field, its molecular arrangement will change, thus affecting the permeability of light, change the voltage can adjust the amount of light through. For the LCD screen, the liquid crystal layer sandwiched between the backlight and the film, adjusts the light that can be passed by adjusting the input voltage, and then through the colored film, you can get different intensity of the three primary colors of light, after mixing is a myriad of colors.
So, how to adjust the input voltage of each pixel?
The so-called TFT(Thin film transistor) is a thin film transistor array on the glass substrate of the LCD panel, so that each pixel of the LCD has its own semiconductor switch, so as to achieve independent and accurate control of "point-to-point". Therefore, the mainstream LCD screen is also called TFT-LCD. IPS and LTPS are different technical implementations of TFT-LCD, which will not be repeated here.
The structure of the OLED screen is much simpler than that of the LCD, which does not require a backlight, nor does it have a liquid crystal and a color filter film, and the internal coating of organic materials is like a small colored light bulb, which can emit light when powered on.
AMOLED: OLED We already know, the previous AM said is the OLED driving mode, its full name is Active Matrix, that is, active matrix, usually using TFT as a switch to control the current through the organic material to achieve different color display. All OLEDs currently used in mobile phones are AMOLEDs, so you can think of them as the same thing.
Super AMOLED: Samsung's improvement to AMOLED eliminates the touch sensing panel in the middle, and puts the AMOLED sensing layer on top of the screen, so the control is more sensitive, thinner, and the brightness is higher, and the presentation effect is better in the sun.
Dynamic AMOLED: It is also Samsung's AMOLED improvement technology, which is currently mainly used in high-end machines. This technology alters the organic material in OLEDs and is said to enable a wider dynamic range, showing more dark details when the contrast between light and dark in the image is high.
In essence, Super AMOLED and Dynamic AMOLED gimmick ingredients are mostly, they belong to AMOLED, and AMOLED is the OLED technology used in mobile phones.
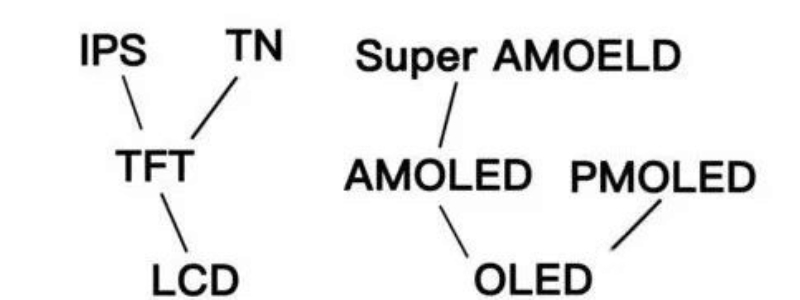
Various subdivided screen technologies under LCD and OLED
Compared with OLED screens, LCD screens have a number of disadvantages.
LCD screens can’t display black: because the liquid crystal layer can’t be completely closed, there are always some backlight will pass through, so the LCD can’t display pure black, can only be displayed as dark gray. OLED, on the other hand, can achieve a pure black display by controlling the switch of each pixel.

The night sky is noticeably darker under the OLED screen (left)
2.Easy to leak light: the backlight of the LCD screen, it is easy to leak out from the screen and the phone's border, forming a light leakage phenomenon, this phenomenon is very common in the era of rough mobile phone workmanship, and it is rarely seen.
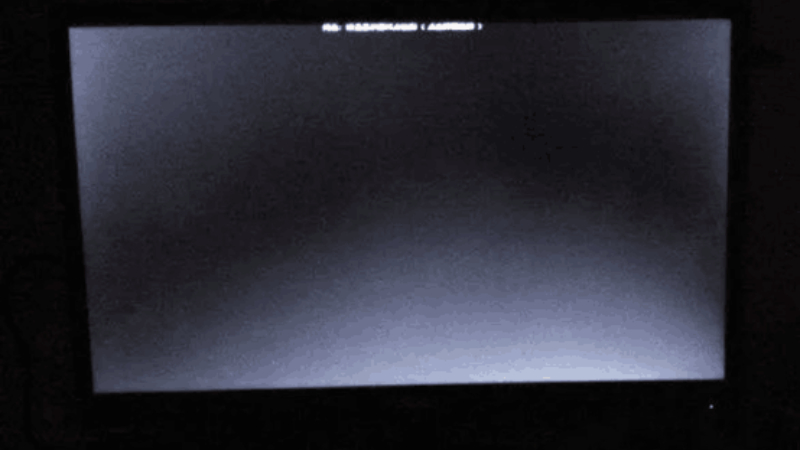

The LCD screen leaks light
3.the screen thickness is large: LCD due to complex technology, limited by the backlight layer and liquid crystal layer, the screen thickness is much larger than OLED. Of course, this thickness is not worth mentioning on the TV, but in the case of the pursuit of thin mobile phones and extremely limited internal space, the screen is thinner, and more other components can be plugged in to improve other aspects of performance.
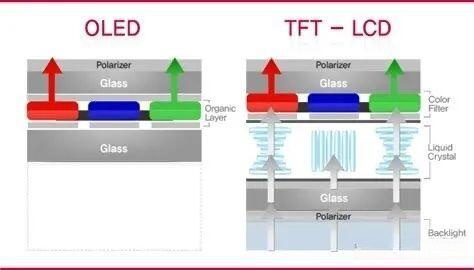
LCD screens are much thicker than OLED screens
4.Difficult to achieve curved screen: LCD can’t bend greatly, and OLED can. Therefore, for those phones with curved screens, they can only use OLED screens.

OLED is ideal for curved screens
5. Large power consumption: Because the LCD screen has a backlight, it must be lit when used, and OLED can control the switch of each pixel separately, so the power consumption of the LCD screen is much larger than that of OLED. The nut R1 and Millet mix2s in the following figure are LCD screens, which are obviously at a disadvantage in terms of battery life under long video playback.
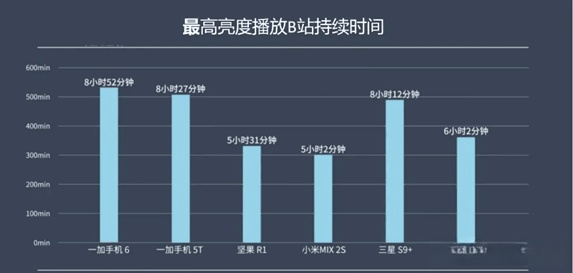
The LCD screen consumes a lot of energy, and the battery life suffers
6. Long response time: LCD screen due to the long response time, when the screen slides quickly will produce a drag. And OLED is responsive, clean and no shadows.
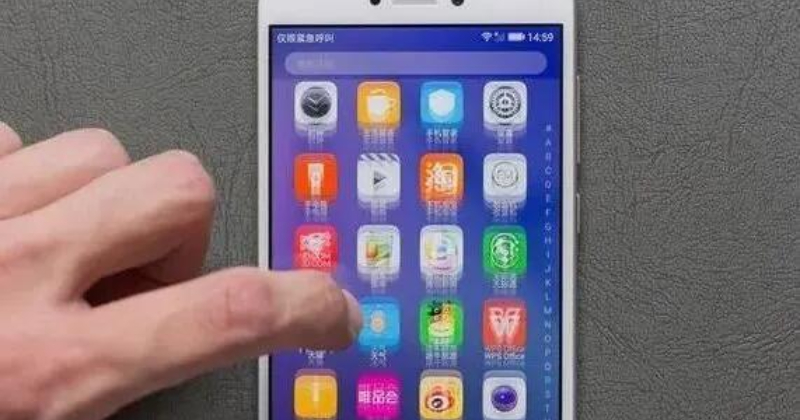
LCD screen dragging phenomenon
Having said so much about the shortcomings of LCD, then, is OLED perfect? Of course not, OLED mainly has the problem of burning screen and stroboscopic.
Burning screen: Because the organic materials used in the OLED screen have a faster aging speed, if some pixels have a large workload and some are relatively idle, there will be a problem of inconsistent aging of the whole screen, resulting in deviations in the color display of different areas. This phenomenon is called screen burning.
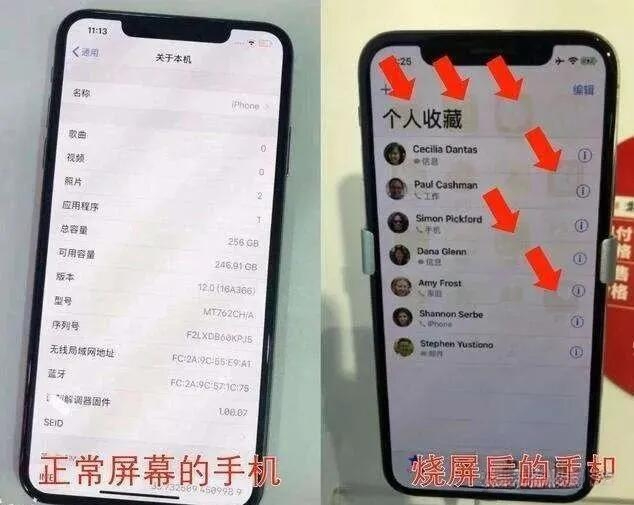
OLED screen burning phenomenon
The burning screen is the disadvantage of OLED screen, for LCD, the backlight is the whole lit, and the aging time of the LCD is longer, so there is basically no problem of burning the screen.
2. Stroboscopic: For LCD, to control the brightness of the screen, directly adjust the brightness of the backlight. But OLED is more troublesome, you need to switch the screen by a high frequency to achieve dimming, want to turn on the screen more times, want to dim the screen more times.
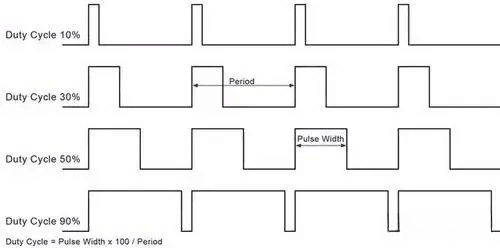
Dimming of OLED screen: The raised part opens for the screen
Since the time of switching the screen is very short each time, although the human eye is difficult to detect each switch change of the screen, it can feel the average light and dark over a period of time, so as to achieve the dimming effect.
For example, to achieve 50% brightness, it is necessary to turn on the screen half of the time, half of the time to turn off the screen, at a lower brightness is to turn off the screen for a longer time, the screen flashes, and even to the point where the naked eye can see: the eyes can’t say the uncomfortable.

Stroboscopic display at low brightness of OLED screen
This phenomenon of OLED is called stroboscopic, which is why it is named "eye screen". In contrast, LCD screens proudly call themselves "eye screens."
Although there are shortcomings, but the defects do not obscure, at present, OLED screens have entered the mainstream, and gradually compress the living space of LCD screens, which is particularly obvious in high-end machines.
In this regard, we can get a glimpse from Apple's configuration.
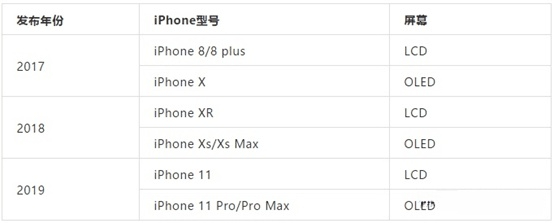
From the above, it can be seen that starting from the X series of Bangs screen, products with high positioning use OLED screens, while those with low prices use LCD.





