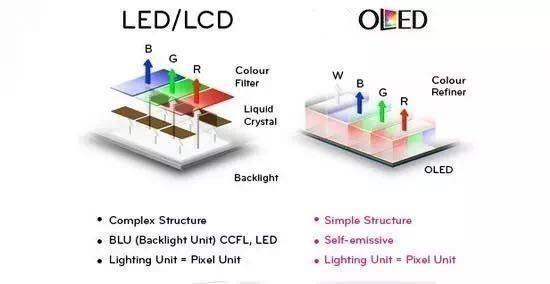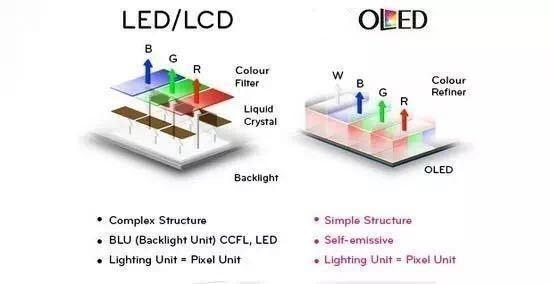
LCD: Backlight Source and OLED: Self -Over Light
The luminous principle of Hispider LCD mainly relies on the backlight layer, that is, the Back-light part in the figure below. This part is usually composed of a large number of LED backlights, which has only one function, that is, to display white light. The white backlight layer has a colored film on top of it. The white backlight penetrates through the colored film to show the color. There is a control valve between the backlight layer and the color film. The part of liquid crystal in the picture below, namely the so-called liquid crystal layer, can control the degree of opening and closing by changing the voltage, control the amount of white light and adjust the ratio of red, green and blue.
Hispider OLED doesn't need a backlight layer like an LCD screen, nor does it need a liquid crystal layer to control the amount of light that comes out. It just needs a power source to light, so OLED is like a screen with an infinite number of small color light bulbs.
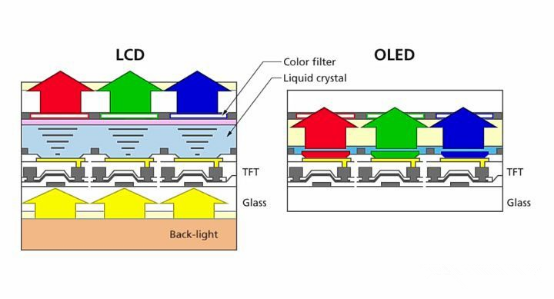
Hispider LCD&OLED’s display for black
LCD has a fatal problem, that is the liquid crystal layer does not close completely. If the LCD shows black, some light will pass through the color layer, so the LCD black is actually a mixture of white and black .
OLED, on the other hand, can display black by turning off the pixels in the black area to achieve an almost pure black effect.

Advantages of Hispider OLED screen
Thickness:
Due to the existence of backlight layer and liquid crystal layer, the thickness of LCD is much thicker than that of OLED, so OLED screen is very easy to make mobile phone or display thin, which is a qualitative leap for mobile phone. Thinner screen allows more components to be crammed into improve the experience of other parts.
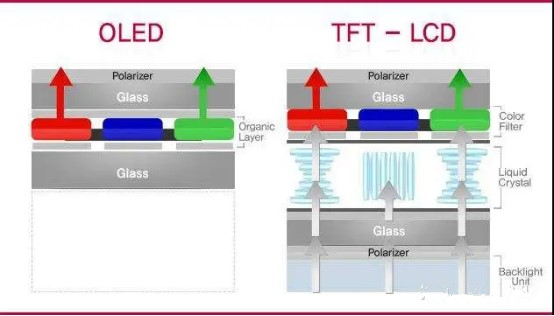
Flexibility:
LCD can't bend much because of the liquid crystal layer and backlight layer, while OLED can fold almost as easily as origami.

Color:
Contrast ratio refers to the ratio of white to black. The higher the contrast ratio, the stronger the color. As LCD has backlight layer, black is not pure black, so the contrast ratio is difficult to be high. OLED black does not emit light, and some pixels in the black area can be directly turned off. Black is almost 0, so the theoretical contrast ratio can be said to be infinite. In a word: OLED is oil painting, pure and delicate color; LCD is watercolor pen painting, the color is hazy and light.

Separate lighting:
LCD on is the entire backlight layer open; Each pixel of OLED is independent, so OLED can light some pixels individually, which can be used to achieve a very convenient function -- aways on display. After the screen is turned off, light up a few pixels at a low brightness to show the time, light up, and notification. This feature greatly reduces the number of times the screen is lit up, which indirectly saves power.

Power consumption:
Because OLED pixels work independently, the light is bright, the dark is dark, and the light is off. LCD is fully backlit no matter what color is displayed, so LCD is bound to consume power. The Nut R1, Mi mix2s and Black Shark in the image below are all LCD screens, which suffer significantly during long video playback.
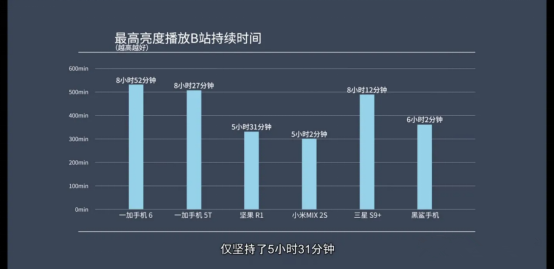
Screen response time:
We know that the color of the picture is displayed by pixels, and it takes time for pixels to change from color 1 to color 2, we call this gray response time. If the gray-scale response time is too long, when the picture slides quickly, the pixel does not have time to change from color 1 to color 2, resulting in residual picture, visual drag will appear, and drag will greatly affect the visual perception. Unlike OLED screens, which barely feel like dragging in everyday use except when white text is displayed on a pure black background, LCD screens, even Apple's top LCDS, are still dragging, and they are also affected by temperature, the lower the temperature, the worse the drag.
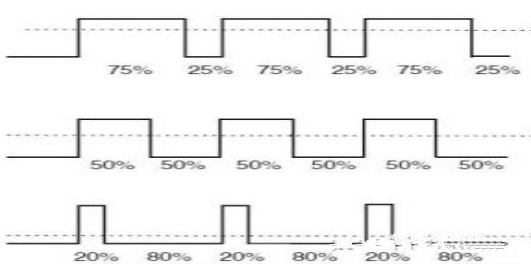
Screen burning:
The defects of OLED are obvious and fatal. LCD screen substrate is inorganic material, while OLED is composed of organic molecular film. The life of organic material is unable to compete with inorganic material, so the life of OLED is inferior to LCD. To make matters worse, OLED is prone to uneven screen aging because each pixel is self-illuminated, rather than the whole block of LCD. This will lead to different working times for each pixel in OLED.

Stroboscopic:
The screen needs to be controlled for brightness. LCD can control brightness (DC dimming) directly by adjusting the voltage of the backlight layer, while OLED will appear uneven jelly effect under low voltage, so OLED can not take control voltage to adjust the brightness, OLED control brightness method is constantly on and off (PWM dimming). PWM dimming adjusts the brightness by changing how long the screen is lit.
Therefore, some people will feel obvious discomfort when using OLED at low brightness, which is caused by the stroboscopic effect of OLED.
Low pixel density: Pixels make up the screen, so the more pixels you have, the sharper the screen will be. The arrangement of pixels on the OLED screen means that the resolution of the two phones will be the same, but the resolution of the screen will be less than a third of the square root. So at the same resolution, OLED screens are not as clear as LCD screens.
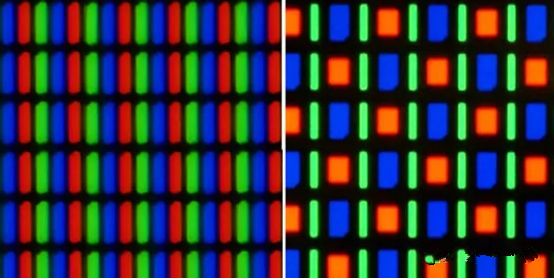
( The LCD screen is arranged with pixels on the left and the OLED screen on the right)
Note: The relevant information of this article is from the Internet. If it infringes, please contact to delete it.