Drawbacks of OLED screens
The first disadvantage: short life span.
The full name of OLED is organic self-luminous diode, the luminous part is the backlight layer, the night layer is only responsible for deflecting and controlling the amount of light, the filter layer is only responsible for changing the color of light, and does not participate in luminescence, the voltage is applied to the LCD screen that does not participate in luminescence, and the OLED screen voltage is directly applied to the self-luminous diode. This causes electrons to migrate frequently in the light-emitting layer of the OLED.

In addition, the luminous layer itself is organic matter, and organic matter is very easy to age compared to inorganic matter. Therefore, organic matter plus frequent electron migration plus self-luminescence directly leads to the life of OLED screen is significantly shorter than LCD screen.
Each pixel of the OLED screen emits light independently, which means that different areas of the screen age at different speeds according to the degree of use. Let's say. Region A displays blue for a long time, and its blue pixels decay faster, so the next time the solid color content is displayed, the blue in that place will be slightly darker, resulting in residual shadows, as if the picture is burned on the screen, this phenomenon is called burning screen. The essence of the burning screen is not to say that the physical layer of the screen is burned, but the screen color difference caused by uneven aging of pixels.
The second disadvantage: dimming mode.
The brightness of the mobile phone screen needs to be controllable, otherwise it is impossible to match the ambient light intensity. At present, there are two main ways to control brightness: PWM and DC. DC dimming is very simple, directly control the voltage to change the brightness of the lamp, the high voltage lamp is bright, the low voltage lamp is dark, DC dimming because the light source is open all the way, there will be no strobe injury to the eye phenomenon.
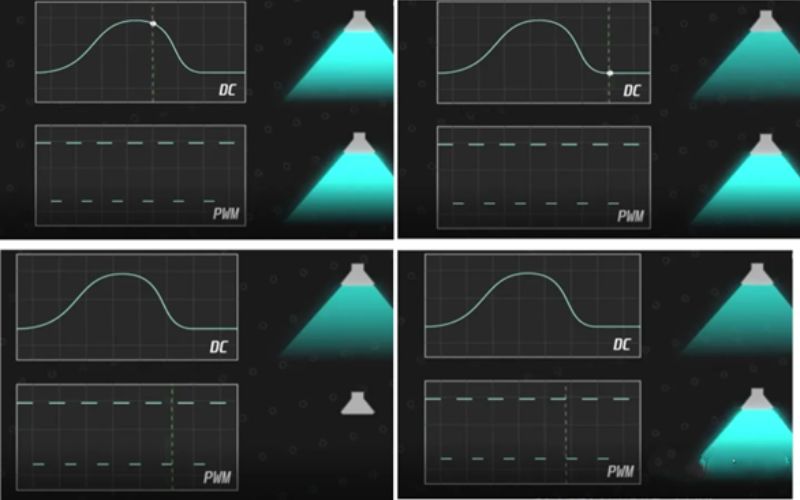
PWM dimming is not the same, PWM uses the adjustment of duty ratio to control brightness. What is adjusted duty cycle? The brightness control is simply on and off. When the frequency of the switch is higher, it looks as if the light is always on. Brightness control, only need to adjust the switch time ratio can be. For example, if a light can be switched on and off ten times a second, its frequency is ten Hertz, and the period of the switch is one Hertz is 0.1 second. PWM dimming has a very big drawback "hurt the eye".
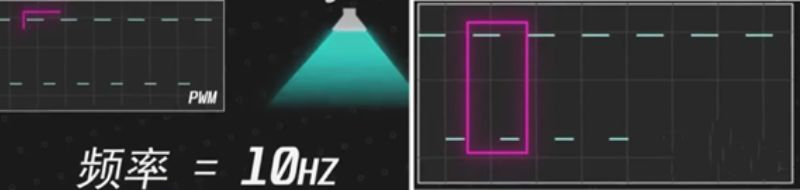
If the PWM frequency is very low, the stroboscopic interval is very easy to be captured by the human eye. If you are in a stroboscopic environment all the time, the eyes will definitely become blurred. But if the PWM frequency is very high, the stroboscopic interval is very short, and the naked eye cannot capture it, the damage to the human eye is much less.
Due to the characteristics of the OLED screen itself, if DC dimming is used, when the brightness is too low, the voltage is too low, the screen will appear as uneven as the rag, and the impact on the display screen is particularly large. So the OLED screen can not use DC dimming, can only use PWM. In addition, because OLED organic materials are easy to age, OLED screens can not use high-frequency PWM dimming, and finally can only use low-frequency PWM.
The third disadvantage: the theoretical resolution does not reach the theoretical clarity.
Resolution is the number of pixels on the screen. It is assumed that in the case of the same screen size, the higher the resolution, the more pixels on the screen, the higher the density of pixels, the higher the clarity. Screen sharpness is measured in PPI. PPI is calculated as the square of the horizontal resolution plus the square of the vertical resolution, and then divided by the size of the screen. Generally speaking, PPI up to 300 is enough, 360 is clear, and 420 is sharp.
However, this calculation formula can only be applied to RGC arranged LCD screens. Not applicable to OLED screens. This needs to talk about the arrangement of sub-pixels, the traditional LCD screen uses the RGD standard arrangement, RDB three sub-pixels are the same size or number, and for the AMOLED screen. Represented by Samsung, the Pentile arrangement is adopted, and the number of green pixels is twice that of red and blue pixels, that is, RGC arrangement, and the area of a single red and blue pixel is larger than that of the green.

In addition, the red and blue pixels arranged by the Pentile are arranged at a 45° right Angle, not horizontally or vertically. In the case of low screen pixel PPI, when displaying horizontal and vertical fonts or pictures, there will be a more obvious jagged feeling. Therefore, after the OLED screen theory is finally fully applied to the above formula, PPI also needs to be multiplied by the square root of 2/3, that is, about 81.65%. In other words, under the same resolution, the screen arranged by Pentile has only 81.65% of the clarity arranged by RGD.
So why the Pentile arrangement? The first reason is to reduce the cost of planting OLED pixels. The second is because of the aging of the OLED screen, the aging speed of the pixels in the three colors of red, green and blue is not the same, so the number and size of the red, green and blue sub-pixels also need to be adjusted accordingly.
As a professional mobile phone replacement screen manufacturer, Hispider not only follows the development of mobile phone screens, but also produces the latest OLED screens, considering the user's demand for cost-effective mobile phone screens, LED mobile phone replacement screens are also in continuous production. The material and quality of the mobile phone replacement screen is also first-class, and I hope it can bring corresponding benefits to you.






